Getting Start
We assume you've fully installed exVim. Go to the Installation if you havn't done it.
Generate .exvim project file
Go to your current working project, for example: ~/foo/bar/foobar/. Generate the .exvim
project under it:
cd ~/foo/bar/foobar/
mvim foobar.exvim # Linux and Windows user will use gvim instead.
You will see windows similar as below:
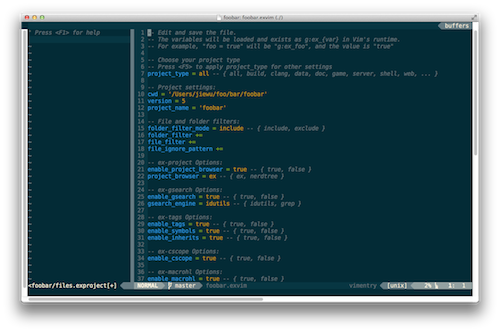
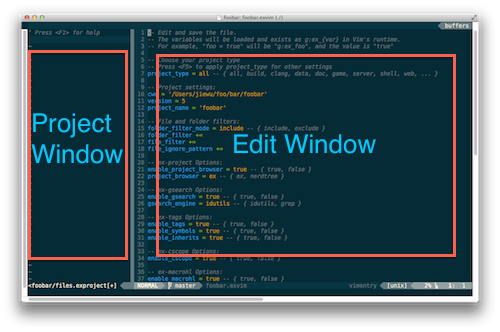
If you check your project directory, there also a hidden folder named .exvim.foobar/
under it. This folder stores all the project files used in exVim for foobar.exvim project.
Note: You can have multiple .exvim files in one project. This allow you to apply
different settings for different purpose.
Build your project tree
Move your cursor to the project window at the left. Press <leader>R [1],
You will see your project files browse in ex-project window like this:
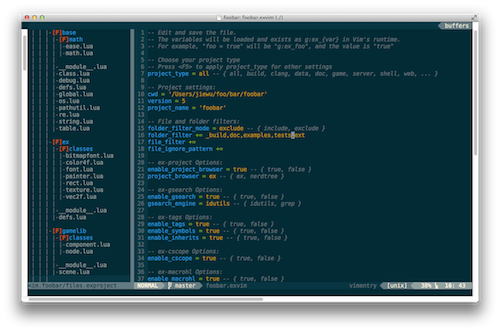
You can also include or exclude the first level folders in your .exvim file. Just go to the
.exvim file, find the folder_filter += lines, and sets your options.
For example:
folder_filter_mode = exclude
folder_filter += _build,_log,_ext
Here I choose 'exclude' mode, and filter out the folders '_build', '_log'
and '_ext' from the project. When you finish editing, type :w to save the .exvim file,
this will trigger Vim refresh the project settings to exVim.
Go back to your ex-project window, and rebuild the tree again by <leader>R [1].
Update your project
By typing :Update commands, you will update exVim project:
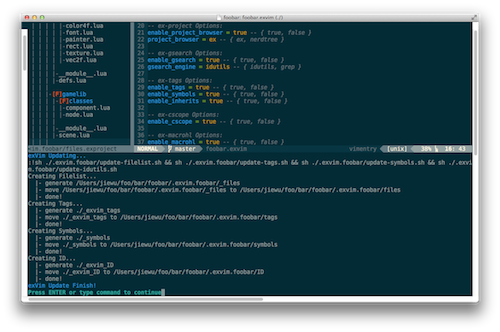
NOTE: Windows users will see a pop-up batch command window instead.
By default, exVim will parse your project with:
- cTags
- id-utils
- cscope
- ...
And generate files store in .exvim.foobar/ for its own use. The files will be used for
exVim plugins such as:
- ex-project
- ex-gsearch
- ex-symobl
- ex-tags
- NERDTree
- AutoComplPop
- ...
Once this is done, exVim will become powerful programming and anlaysis tools for your project.
NOTE: When you changes your projects, you probably need to manually :Update again, exVim
use static analysis for project, it will not detect increament changes, this is because we think
performance is imporatant and from our experience, manually :Update is not so bad.
Userful commands
Now that you have unleash the power of exVim, let's try something quickly:
| Commands | Usage |
|---|---|
<leader>gg |
Global search current word under cursor, show the result in ex-gsearch window. |
<leader>] |
Search the defines and declarations of current word under cursor, show the result in ex-tags window. |
<leader>sg |
List all defines and declarations of current word, show the result in ex-symbole window. |
:GS <word> |
Global search |
In the ex-gsearch, ex-symbol window, you search a pattern by Vim's / command, and filter the search result with <leader>r.
Remember, you can use the commands above in any ex-plugin window, which means:
- you can global search a word in ex-project window
- you can list symbols in gsearch results
- you can jump to a tag in ex-symbol window
- ...
Just use them freely to filter and locate your final result.
For more details about exVim plugins, read Plugins. You can also check ex-project, ex-gsearch, ex-symbol, ... for the details of each plugin, and their configurations.
Footnotes
<leader>Rhere means press key\, then pressshift+r(uppercase “r”). vim recommend 3rd-party plugins use<leader>(aka.\) to begin their operations, also the operations in vim are case sensitive.
